Introduction
The data storage sector is about to be disrupted, with decentralised blockchain-based cloud storage technology providing a compelling alternative to centralised storage solutions that have been around for decades.
Every dynamic business, large or small, requires data storage. Business data is crucial and sensitive, ranging from financial reports to customer details. This information is used to inform decision-making processes. Businesses, on the other hand, must store their data in a secure and dependable location.
As a company grows, so does the amount of data collected. Higher data volumes necessitate increased complexity in terms of storing, processing, analysing, and retrieving information. To streamline their operations, businesses are increasingly depending on centralised storage solutions such as the cloud. However, given the drawbacks of the cloud and the highly volatile nature of technology, we doubt that the centralised storage solution is here to stay.
Before we explore the potential solutions supplied by decentralised blockchain storage technology, let’s take a look at the existing industry dynamics and the challenges they cause.
How do businesses currently store data?
We’ve already come a long way from the conventional and bulky paper-file storage system to today’s more flexible and reliable digital alternatives. Cloud-based centralised storage technology has outperformed local physical storage devices such as hard discs and servers. Today, about 94% of all enterprises employ centralised cloud solutions for data storage.
Users can store data via the internet and access it remotely from anywhere, at any time. The data is stored in a centralised location, such as the cloud. As a result, it provides easy access, mobility, and quick deployment across all devices, as well as backups and unlimited storage – all at a low cost. Large corporations such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Samsung, Alibaba, and Apple are now offering cloud storage options via Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS).
We’ve seen a lot of activity in these domains since the COVID-19 crisis made remote work the new normal. Despite this rising trend, 75% of organisations are concerned about the security of their confidential data kept in the cloud.
Concerns about Centralized Storage Systems
While implementing and managing a centralised cloud storage system, businesses encounter the following issues.
Increasing storage costs
Enterprises no longer need to invest in servers and costly infrastructure for data storage thanks to centralised storage systems. Cloud service providers, on the other hand, charge astronomical fees for bandwidth transmission and data security. Additionally, hiring expertise or migrating from one cloud vendor to another becomes costly for enterprises.
Data breaches and security risks
In 2020, the Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report (DBIR) identified 32,002 security events and 3,950 data breaches, with 58% of data breaches containing personal data. Almost every major industry player has reported data breaches in the last few years. Cloud servers that are centralised are almost always housed in a single location. In the event of a power outage, the entire network could become paralysed, resulting in the loss of previously saved data chunks.
Low transmission speed
Centralized servers are situated in faraway locations, far from the user’s business. The transmission speed is slowed due to the distance constraint. As a result of these challenges, businesses all over the world are looking for faster, more secure, and less expensive ways to store their ever-increasing volumes of data.
Blockchain in Cloud Storage
The internet has been completely altered by blockchain technology. Blockchain technology, which was first utilised for Bitcoin, has since expanded to include video/audio streaming, smart contracts, social media, and much more. This adaptable and secure technology can also be used for cloud storage by businesses. Let’s take a look at what blockchain is and how it works before we get into how it operates.
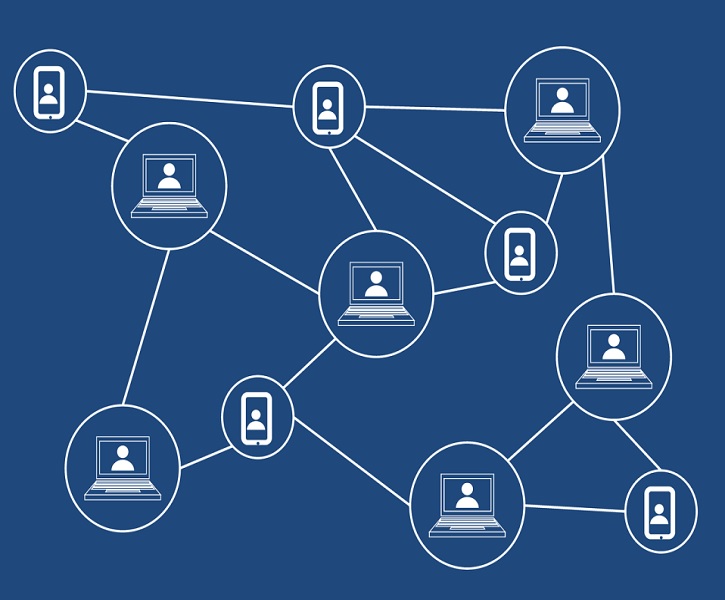
A peer-to-peer networking infrastructure underpins blockchain. This obviates the need for a central administrative authority. Ordinary people, known as miners, are in charge of running the system. Blockchain, in essence, distributes and stores data in blocks that are validated by miners or peers and encrypted using public-private keys and hash codes. Every block that is created is validated, making it nearly impossible to modify or cheat the ledger. The block becomes invalidated if an attacker tries to manipulate the data. As a result, blockchain remains secure and manageable.
Simply explained, a blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed over a network of computers. Blockchain in cloud storage takes some of the blockchain’s capabilities and combines them with a typical centralised storage system to create a secure, decentralised data storage system.
The user’s data is broken down into smaller bits, encrypted using hash codes and public-private keys, copied, and stored in numerous locations across a network of connected devices using blockchain cloud storage.
Blockchain cloud storage is edging closer to becoming its own business model. It allows a variety of small businesses to join the cloud storage network by contributing their computing power and storage space. As a result, all parties involved get compensated for their contributions, and the overall cost of cloud storage decreases.
What is Decentralized Blockchain Storage?
Users may save their information without relying on massive, centralised data silos like the cloud, thanks to the decentralised storage system. Since it became clear that centralised storage systems were eroding basic but important principles like privacy and security, the idea of decentralisation in data storage has gained traction.
Decentralized storage solutions rely on a peer-to-peer network of users who each store small, encrypted chunks of the overall data. As a result, a reliable data storage and sharing system have been created. It could be based on a blockchain or any other peer-to-peer network.
How does Blockchain-based decentralized cloud storage work?
Users’ files are divided into several little bits of data called “blocks”. The blocks are subsequently encrypted with a unique hash or public-private keys and distributed among different computers, or “nodes.” “Sharding” refers to the process of distributing data over a network of nodes.
It’s important to note that the blockchain-based storage system does not really store data on the blockchain. Instead, user groups are encouraged to join, store, and host servers. A number of tiny entities join the network by contributing processing power and storage space.
Similarly, all data is dispersed and kept in multiple locations. Interlopers who try to break into these places will only be able to get a portion of the information, not the complete file. To summarise, data security is ensured through blockchain-based decentralised storage systems.
No personal information about the user in the data in these installations. Miners, in any case, only get little portions of the entire file. When users attempt to retrieve their files, all data chunks are validated first. The miner is removed from the network if something has been changed. The system retrieves and displays the modified portion from a redundant duplicate of the original file kept in multiple locations, alleviating users’ concerns.
To protect and speed up data storage and retrieval, the decentralised system uses load balancing and data redundancy. Because it maintains numerous copies of the original data in multiple locations, the user is not affected if one machine fails. By preventing traffic from concentrating on a single area, the load balancing system optimises the overall network. Users can participate in the decentralised storage network using platforms such as Filecoin, Sia, MaidSafe, and Storj.
Benefits of Decentralized Blockchain Storage
To protect and speed up data storage and retrieval, the decentralised system uses load balancing and data redundancy. Because it maintains numerous copies of the original data in multiple locations, the user is not affected if one machine fails. By preventing traffic from concentrating on a single area, the load balancing system optimises the overall network.
- High reliability
- Lower costs
- Increased speed
- Load balancing
- Fair market pricing
- Increased security and privacy
Final Verdict
From big tech corporations to entrepreneurs, several companies have jumped to the blockchain cloud storage market, transforming their businesses digitally. Blockchain development companies are constantly on their toes to improvise the decentralised data storage space to avoid the pitfalls of conventional and centralized cloud data storage which concerns increasing storage costs, data breaches and security risks, low transmission speed.
We will soon bid goodbye to the centralized oligopolies which have failed in enabling us to make the most of our data. According to PR Newswire, the popular distributor of press releases, the data storage market is expected to grow to $88.91 billion by the year 2022. Having said that, blockchain will be vital to the rest of the decentralised storage business, as it is quickly becoming a hot space because of the scalability, efficiency, better security, and affordability that blockchain provides in today’s more data-thirsty and data-heavy world.
Blog Suggestion : How to create an NFT on OpenSea

Leave a Reply